This repository contains solutions of Problem 2.24 and 4.25 from the textbook Operating System Concepts 10th Edition by Abraham Silberschatz, Peter Baer Galvin and Greg Gagne.
- Name: Dev Agrawal
- Roll No: 201ME169
In Section 2.3 (System Calls), we described a program that copies the contents of one file to a destination file. This program works by first prompting the user for the name of the source and destination files. Write this program using either the POSIX or Windows API. Be sure to include all necessary error checking, including ensuring that the source file exists. Once you have correctly designed and tested the program, if you used a system that supports it, run the program using a utility that traces system calls. Linux systems provide the strace utility, and macOS systems use the dtruss command. (The dtruss command, which actually is a front end to dtrace, requires admin privileges, so it must be run using sudo.) These tools can be used as follows (assume that the name of the executable file is FileCopy: Linux: strace ./FileCopy macOS: sudo dtruss ./FileCopy Since Windows systems do not provide such a tool, you will have to trace through the Windows version of this program using a debugger.
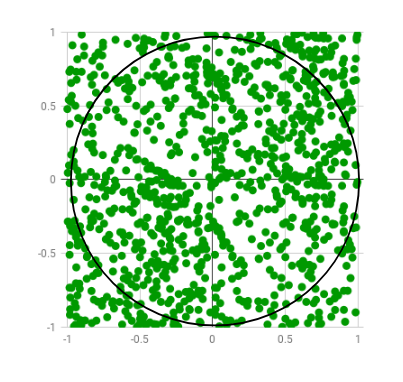
An interesting way of calculating π is to use a technique known as Monte Carlo, which involves randomization. This technique works as follows: Suppose you have a circle inscribed within a square, as shown in Figure 4.25. (Assume that the radius of this circle is 1.)
• First, generate a series of random points as simple (x, y) coordinates. These points must fall within the Cartesian coordinates that bound the square. Of the total number of random points that are generated, some will occur within the circle.
• Next, estimate π by performing the following calculation: π = 4 × (number of points in circle) / (total number of points)
- (Reason: Area of Square / Area of circle = (2r)2/πr2 = 4/π)
Write a multithreaded version of this algorithm that creates a separate thread to generate a number of random points. The thread will count the number of points that occur within the circle and store that result in a global variable. When this thread has exited, the parent thread will calculate and output the estimated value of π. Use OpenMP to parallelize the generation of points. Be careful not to place the calculation of π in the parallel region, since you want to calculate π only once.
It is worth experimenting with the number of random points generated. As a general rule, the greater the number of points, the closer the approximation to π.
- Open MP Documentation
- Calculating pi with Monte Carlo using OpenMP by Codereview
- Estimating the value of Pi using Monte Carlo
- C Code for copying and pasting contents of a file
- Copy File Contents - Constitution of India
- Strace commands in Linux
- getpid() documentation
- System Calls Documentation
- Linux Documentation
- OpenMP and GCC Installation Guide
- 2.19.5.4 reduction Clause
- Time command in Linux with examples
For any queries or feedback, please feel free to reach out.