DevOps Essentials
- A combination of “development” and “operations”, DevOps removes the silos between these two traditionally separate disciplines.
- DevOps involves building, using and maintaining systems and applications.
- DevOps is a methodology that allows a single term to manage the entire application development life cycle, that is development, testing, deployment and operations
- DevOps is a software development approach through which superior quality software can be developed quickly and with more reliability.
- The objective of DevOps is to shorten the system’s development life cycle through:
- Automate for Build & Testing (Continuous Integration)
- After a code commit, Continuous Integration builds and tests the app right away.
- Docker Containers can be used to simulate the test environment at this phase.
- The automation testing can be handled by Selenium, and the reports can be generated by TestNG.
- Automate Deployment (Continuous deployment)
- The software release process that uses automated testing to validate if changes to a codebase are correct and stable for immediate autonomous deployment to a production environment.
- Automate Monitoring & Issue Tracking (Continuous Monitoring)
- The software's usage is meticulously logged and analyzed in order to spot trends and pinpoint trouble areas.
- Automate Feedbacks (Continuous Feedback)
- By analyzing the results of the software's activities, the application development is constantly improved by establishing a key phase of constant feedback between operations and the development of the present software application's future iteration.
- With the rise of Agile software development models, DevOps has grown in prominence in recent years.
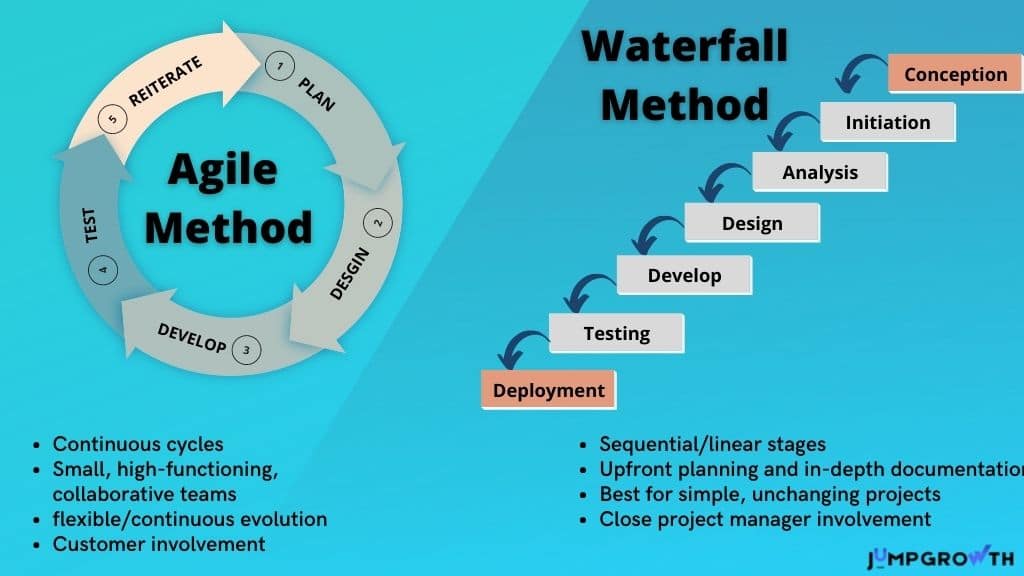
- Waterfall Model methodology which is also known as Liner Sequential Life Cycle Model.
- Waterfall Model is followed in a sequential order, so project development team only moves to next phase of development or testing if the previous step is completed successfully. What is the Agile methodology?
- Agile methodology is a practice that helps continuous iteration of development and testing in the software development process.
- In this model, development and testing activities are concurrent, unlike the Waterfall model.
- This process allows more communication between customers, developers, managers, and testers.
- Waterfall is a Liner Sequential Life Cycle Model whereas Agile is a continuous iteration of development and testing in the software development process.
- In Agile vs Waterfall difference, the Agile methodology is known for its flexibility whereas Waterfall is a structured software development methodology.
- Comparing the Waterfall methodology vs Agile which follows an incremental approach whereas the Waterfall is a sequential design process.
- Agile performs testing concurrently with software development whereas in Waterfall methodology testing comes after the “Build” phase.
- Agile allows changes in project development requirement whereas Waterfall has no scope of changing the requirements once the project development starts.
- Waterfall is a more traditional approach to project management, involving a linear flow.
- Waterfall is best for projects with concrete timelines and well-defined deliverables. If your major project constraints are well understood and documented, Waterfall is likely the best approach.
- Agile, on the other hand, embraces an iterative process.
- The Agile methodology was created for projects where the significant constraints are not well understood. If your project involves developing a new product, the scope and timeline may be difficult to determine in advance. Agile is flexible, enabling you to plan a project in stages or “sprints” to evolve as the work progresses.
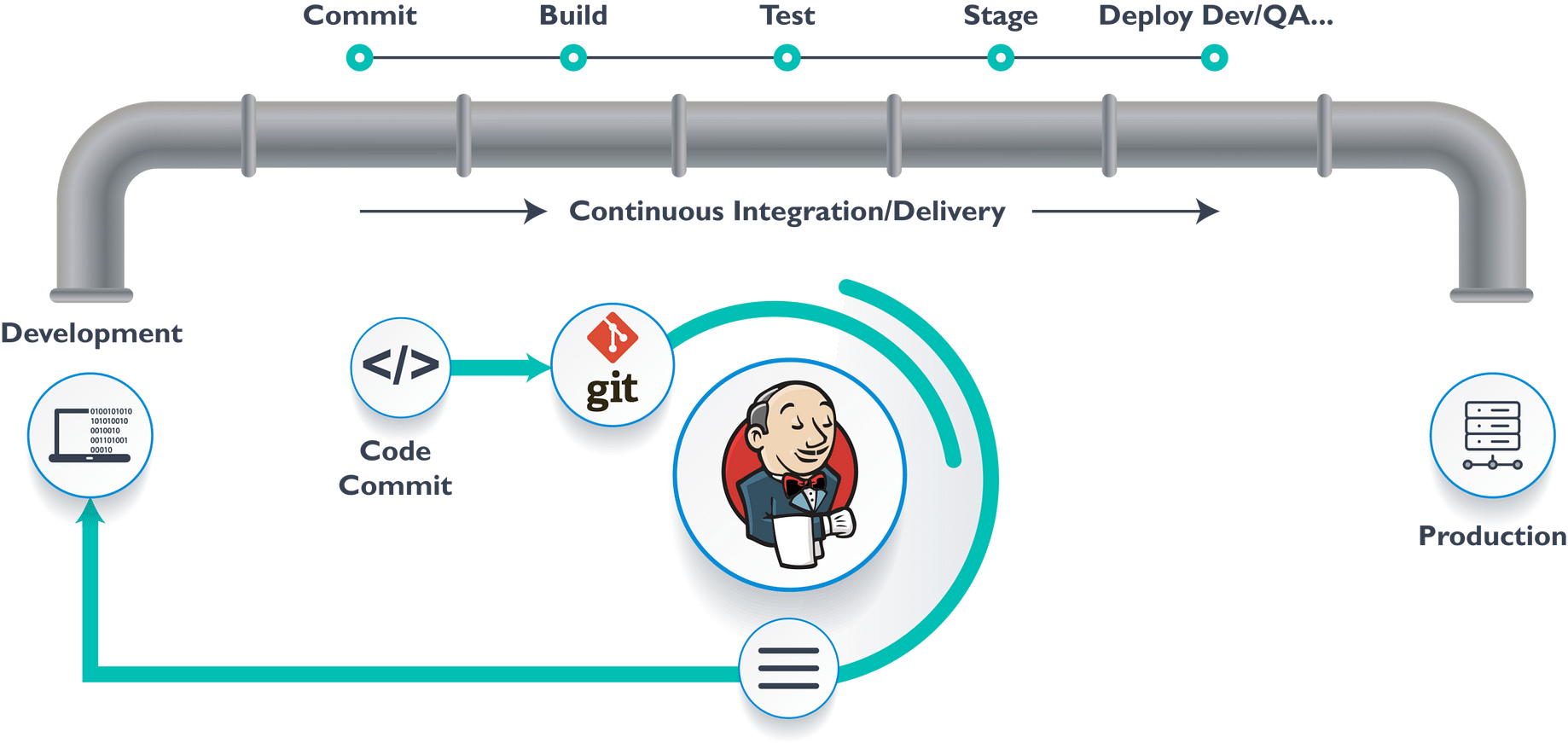
- CI/CD is a method to frequently deliver apps to customers by introducing automation into the stages of app development.
- The main concepts attributed to CI/CD are continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment.
- Jenkins is an open source project written in Java.
- The leading open source automation server.
- It helps to perform a chain of actions to achieve the Continuous Integration process in an automated fashion.
- For example, if your team is developing a project, Jenkins will continuously test your project builds and show you the errors in early stages of your development.
- After a code commit, Continuous Integration builds and tests the app right away. Commits are made often throughout the day in a large project with numerous developers.
- Each commit results in the creation and testing of code. The build is then tested for deployment if the test passes. The code gets pushed to production if the deployment is successful.
- This continuous process of commit, build, test, and deploy is known as continuous integration/deployment.
- Virtualization is a process whereby software is used to create an abstraction layer over computer hardware that allows the hardware elements of a single computer to be divided into multiple virtual computers.
- A virtual machine is an emulation of a physical computer. VMs enable teams to run what appear to be multiple machines, with multiple operating systems, on a single computer.
- VMs interact with physical computers by using lightweight software layers called hypervisors.
- Hypervisors can separate VMs from one another and allocate processors, memory, and storage among them.
- Docker is an open source software development platform for building, deploying, and managing containerized applications.
- It helps to separate infrastructure and applications in order to deliver software quickly.
- Docker uses resource isolation in the OS kernel to run multiple containers on the same OS. This is different than virtual machines (VMs), which encapsulate an entire OS with executable code on top of an abstracted layer of physical hardware resources.
- Unlike Hypervisors, which are used for creating VM (Virtual machines), virtualization in Docker is performed on system-level, also called Docker containers.
- As you can see the difference in the image below, Docker containers run on top of the host’s Operation system. This helps you to improve efficiency and security.
- Moreover, we can run more containers on the same infrastructure than we can run Virtual machines because containers use fewer resources.
- Docker in 100 Seconds Learn Docker in 7 Easy Steps - Full Beginner's Tutorial
- Docker Tutorial for Beginners [FULL COURSE in 3 Hours]
- Deploying a MERN Application (with Docker, Atlas, and Digital Ocean!)
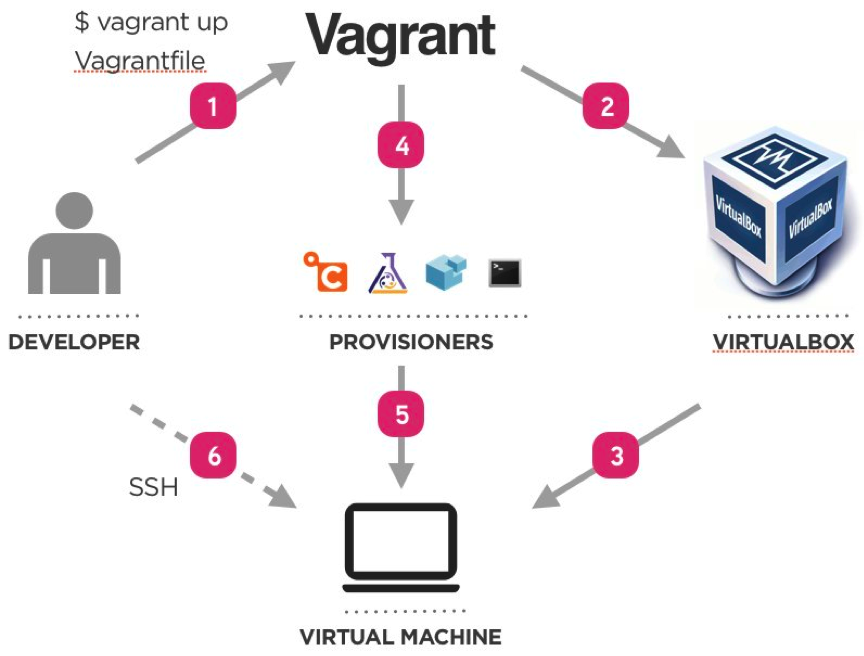
- Vagrant is an open-source tool that helps us to automate the creation and management of Virtual Machines.
- Vagrant will isolate dependencies and their configuration within a single disposable, consistent environment, without sacrificing any of the tools we use.
- Vagrant is used to set up one or more virtual machine by:
- Importing pre-made images called boxes
- Setting VM-specific settings
- Running provisioning software like Puppet or Chef
- Once the entire development environment is ready, vagrant creates a single file called “Vagrantfile”.
- The Vagrantfile describes the type of machine required for a project and how to configure and provision these machines.
- With the help of Vagrantfile, other members of a team can create their development environments from the same dependencies and configuration, so that all team members can run the code in the same environment.
- you need to learn Ansible RIGHT NOW!! (Linux Automation)
- Chef Tutorial | Chef Tutorial For Beginners | DevOps Chef Tutorial | DevOps Tools | Simplilearn
- Puppet Full Course | Learn Puppet Step By Step | Puppet Tutorial For Beginners | Simplilearn
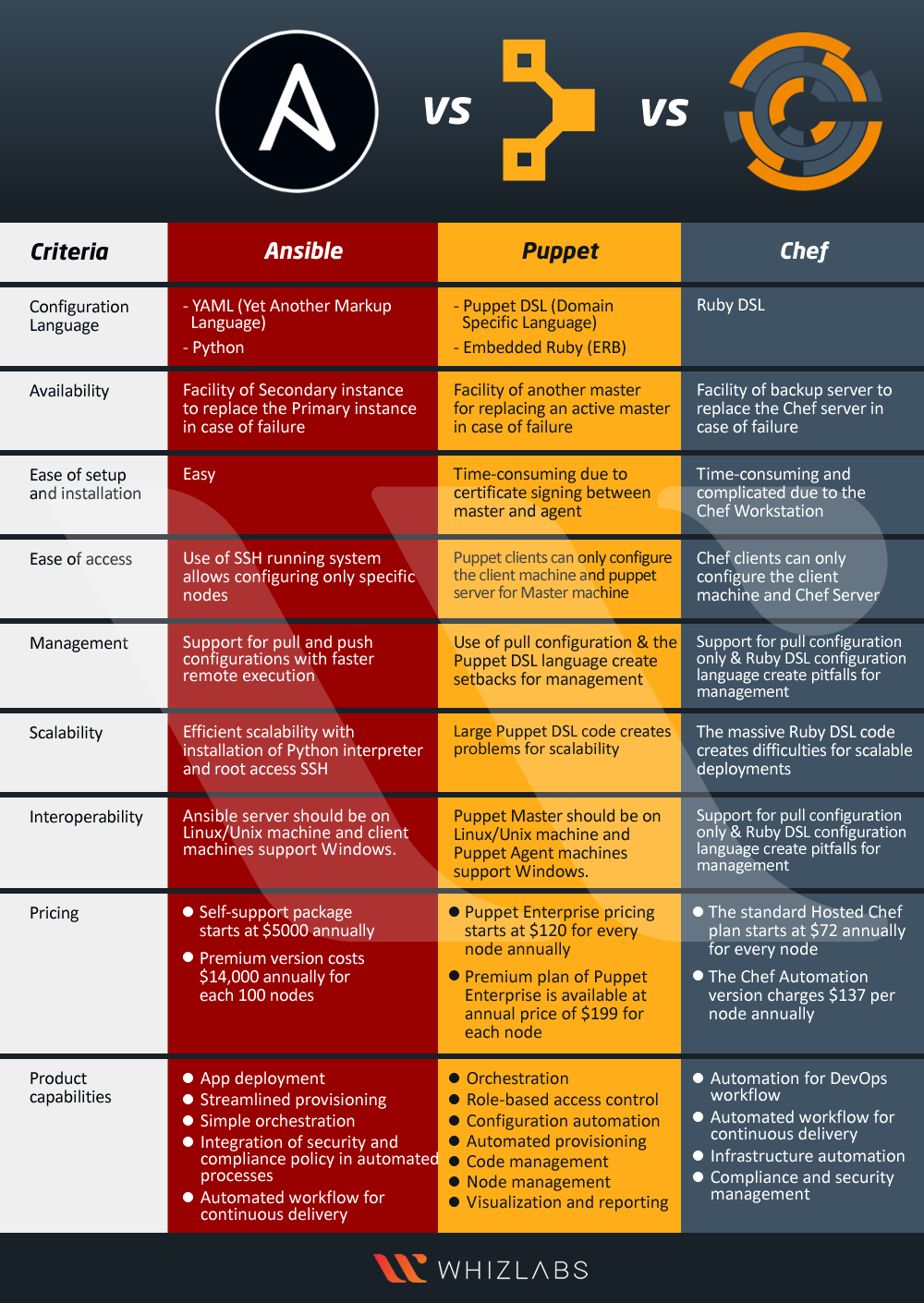
- Chef vs Puppet vs Ansible vs Saltstack | Configuration Management Tools | DevOps Tools | Simplilearn
- DevOps Training
- DevOps Tools
- Simplilearn Skillup Free Courses in DevOps
- The Linux Foundation Trainings